Great Discoveries of the Bible
— A Landmarks of Faith Seminar —

Lecture #3a Audio
 See notes below.
See notes below.Lecture #3a:
Or click here for more listening options at Internet Archive.
__________________________
Lecture #3a Notes
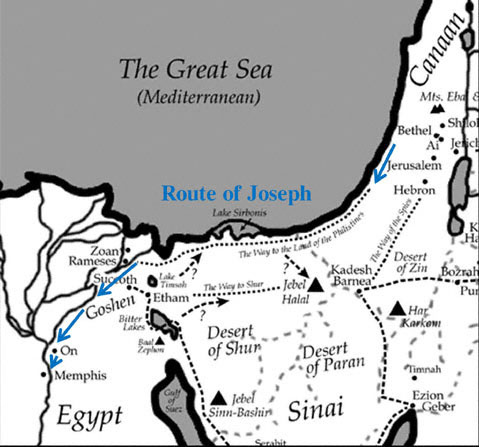
LIFE IN EGYPT AND CANAAN
Discovery: A tomb painting that shows thirty-seven Semites (Semitic people) bringing black eye paint (kohl) to trade in Egypt (the tomb of Khnumhotep, at Beni Hasan, 150 miles south of Cairo, c. 1850 BC).
Sinuhe: The central character in a famous Egyptian story (c. 1875 BC). Sinuhe escapes from Egypt to Canaan, but later returns to Egypt. His story gives us insight into the experience of Joseph and later of Moses.
Shur (Wall
): A line of fortresses along the eastern border of Egypt to protect it from desert raiders. The desert east of this line was known as the Desert of Shur (see Gen. 16:7, 20:1, 25:18; Exo. 15:22; 1 Sam. 15:7, 27:8).
EGYPTIAN HISTORY (B.C.)
- OLD KINGDOM (3100-2190)
- 1st-2nd Dynasties: Unification of Egypt
- 3rd-6th Dynasties: Age of the Pyramids
- First Intermediate (2190-2052)
- 7th-10th Dynasties: Disorder
- MIDDLE KINGDOM (2052-1778)
- 11th Dynasty: Reunification
- 12th Dynasty: Joseph
- Second Intermediate (1778-1570)
- 13th-14th Dynasties: Disorder
- 15th-17th Dynasties: Hyksos rule in north
- NEW KINGDOM (1570-1200)
- 18th Dynasty: Hyksos driven out, Slavery, Moses, Exodus, Conquest
- 19th Dynasty: Mernepthah Stele that mentions Israel in Canaan (1209)
Bedu: Egyptian term for the Bedouin living in Canaan. Also called the Sand-Crossers.
EGYPTIAN INFLUENCES ON JOSEPH
Gen. 41:14: And when he had shaved himself...
Gen. 41:45: Then Pharaoh named Joseph Zaphenath-paneah; and he gave him Asenath, the daughter of Potiphera priest of On [Heliopolis], as his wife
Gen. 44:2,5: And put my cup, the silver cup, in the mouth of the sack of the youngest
.... Is not this the one from which my lord drinks, and which he indeed uses for divination?
Mummification: The process of turning a human body into a mummy.
Gen. 50:2-3: And Joseph commanded his servants the physicians to embalm his father... Now forty days were required for it, for such is the period required for embalming
Gen. 50:10,13: When they came to the threshing floor of Atad, which is beyond the Jordan, they lamented there with a very great and sorrowful lamentation; and he [Joseph] observed seven days mourning for his father.... and buried him in the cave of the field of Machpelah by Mamre [Hebron]
In Egypt, the east bank of the Nile River was considered the side of life. The west bank was the side of death, where people were buried and where the Egyptian pyramids are located.
Gen. 50:26: So Joseph died...and he was embalmed and placed in a coffin in Egypt
Gen. 43:32: So they served him [Joseph] by himself, and them [his brothers] by themselves, and the Egyptians who ate with him, by themselves; because the Egyptians would not eat bread with the Hebrews, for that is an abomination to the Egyptians
Gen. 46:34: ...That you may live in the land of Goshen; for every shepherd is an abomination to the Egyptians
AFTER THE TIME OF JOSEPH
Hyksos: Semitic rulers of northern Egypt. Their cultural power base was Canaan, which for a short period became strong enough to dominate northern Egypt.
Exo. 1:10: ...Lest they [the Israelites] multiply and in the event of war, they also join themselves to those who hate us...
Exo. 2:23: The sons of Israel sighed because of the bondage, and they cried out; and their cry for help...rose up to God
SLAVERY IN EGYPT
Exo. 1:11,14: And they built for Pharaoh storage cities.... with hard labor in mortar and bricks
Papyrus (plural: Papyri): A type of paper made from papyrus reeds. (Origin of the English word paper.
)
Discovery: Papyri from the time of Moses that mention the daily brick quotas for slaves and even the occasional lack of straw for making bricks (Exo. 5:7-8).
Discovery: Tomb paintings that show Egyptian slaves of various nationalities smelting copper.
PALEO-HEBREW ALPHABET
𐤕 𐤔 𐤓 𐤒 𐤑 𐤐 𐤏 𐤎 𐤍 𐤌 𐤋 𐤊 𐤉 𐤈 𐤇 𐤆 𐤅 𐤄 𐤃 𐤂 𐤁 𐤀
Serabit el-Khadim: Ancient Egyptian mining site in western Sinai. Some of the earliest examples of alphabetic writing were found here, carved by Semitic slaves into the walls of the mines.
Timnah Valley: Ancient Egyptian mining site in southern Israel.

Hathor: The goddess of foreign lands, as well as of mining. A cow goddess, often shown as a woman with cow-like ears.
How did people become slaves in the Ancient Middle East?
- 1) Some were captives of war: both soldiers and civilians.
- 2) Others were kidnapped and sold on the slave market—like Joseph. This is forbidden in the Law of Moses (Exo. 21:16:
He who kidnaps a man, whether he sells him or he is found in his possession, will surely be put to death
). - 3) Sometimes people sold their own children (2 Kings 4:1:
The creditor has come to take my two children to be his slaves
). - 4) If they didn’t have children, they might sell themselves, out of hunger or debt (Lev. 25:39:
And if a countryman of yours becomes so poor...that he sells himself to you...
)
Exo. 21:26: If a man strikes the eye of his male or female slave, and destroys it, he will let him go free...
Exo. 21:20: If a man strikes his male or female slave with a rod and he dies at his hand, he will be punished
Deut. 23:15: You will not hand over to his master a slave who has escaped from his master to you
Exo. 20:2: I am the Lord your God, who brought you out of the land of Egypt, out of the house [or place] of slavery
Deut. 15:12: ..in the seventh year you will set him free
DATING THE EXODUS
The names of the pharaohs were often composed of the names of Egyptian gods: Ramesses means Ra (the sun god) gave birth to him.
Amenhotep means Amon (the name of a god) is satisfied.
2 Sam. 2:8: And Abner, the son of Ner, commander of Saul’s army had taken Ish-bosheth the son of Saul...
(called Ish-baal in 1 Chron. 8:33).
1) The most popular date for the Exodus is about 1250 BC, in the time of Ramesses II (19th dynasty).
Exo. 1:11: They built for Pharaoh storage cities, Pithom and Ramesses
Surface survey: Examining archeological materials lying on the surface of a site or area without excavation. From the types of pottery visible, archeologists can usually get an idea of when the site was inhabited.
Nelson Glueck: Did a surface survey of Jordan in the 1930’s. He claimed there was no evidence for the Edomite, Moabite, and Ammonite peoples before 1300 BC. Excavations since that time have overturned Glueck’s findings.
EGYPT’S 18TH DYNASTY
- Amosis (1570-1546): Hyksos (foreign rulers) expelled from Egypt. Israelites made slaves.
- Amenhotep I (1546-1526): Slavery continues.
- Thutmose I (1526-1512): Israelite baby boys ordered to be killed. Moses born (1526). Saved by Hatshepsut (Thutmose’s daughter), who had no male child.
- Thutmose II (1512-1504): Moses raised at court. Hatshepsut is queen.
- Hatshepsut (1503-1483): Moses’ step-mother rules as regent for Thutmose III after the death of her husband.
- Thutmose III (1504-1450): Son of a concubine; younger than Moses. Moses flees to Midian. Hatshepsut’s image and name erased from monuments (because of her association with Moses?). Thutmose conducts 20+ military campaigns into Canaan, subduing the land again for Egypt.
- Amenhotep II (1450-1425): Exodus (1446). After Amenhotep’s 4th year (the date of the Exodus) Egyptian invasions of Canaan cease (because of the destruction and turmoil of the plagues).
- Thutmose IV (1425-1417): Israelites wander in the desert. Thutmose is not Amenhotep’s eldest (who was killed in the plagues), but a younger son who did not expect to reign. Only one northern campaign. Peace treaty established with Mitanni against the Hittites.
- Amenhotep III (1417-1379): Israelite conquest of Canaan (begins 1400). Amarna Letters start to appear concerning the invading Habiru. No Egyptian military response.
- Amenhotep IV (1379-1362): Israelite conquest continues. More Amarna Letters about the Habiru. Still no military response. Egyptian army called back to Egypt to help with religious reforms that allow worship of only one god (due to a loss of faith in the old gods as a result of the plagues?)
- Tutankhamun (1361-1352): Restores ancient worship. His unrobbed tomb (the tomb of King Tut) was discovered in modern times.
- Ay (1352-1348)
- Horemheb (1348-1320)
2) The Biblical date for the Exodus is 1446 BC, in the reign of Amenhotep II (18th dynasty).
Hatshepsut: A female pharaoh who ruled wearing an artificial beard. She may have been the young lady, then a royal princess, that rescued baby Moses from the river. Why would she take such a risk? She had no male child of her own, which threatened her position in the royal court.
Thutmose II: Pharaoh and husband of Hatshepsut. Just before his death, he named the son of one of his concubines to be the new pharaoh (Thutmose III). But since Thutmose III was very young, Hatshepsut ruled in his place for twenty years.
Exo. 2:15: When Pharaoh heard of this matter, he tried to kill Moses...
MIDIAN
Midianite Connection: A theory that traces Moses’ ideas about religion to the Midianites, among whom he lived for forty years in the desert.
Discovery: A Midianite temple at Timnah with standing stones (matzeboth). It was a tent shrine. The tent was found rolled up and buried to the side of the shrine. A small bronze snake was also discovered (Num. 21:9).
There’s no question that Moses learned much about God in the desert. In addition to whatever he may have learned from the Midianites (from Jethro), he also had his own experiences with God, like the encounter at the burning bush.
Exo. 3:2: And the angel of the Lord appeared to him in a blazing fire from the midst of the bush...
Exo. 3:4: When the Lord saw that he turned aside to look, God [Elohim] called to him from the midst of the bush...
PLAGUES
Amenhotep II: The pharaoh of the Exodus. Ruled from Memphis, which was near Goshen.
Thutmose IV: Son of Amenhotep II, who recorded in an inscription (known as the Dream Stele
) that his advancement to the throne was an unforeseen blessing of the gods. This matches the Bible, which says that the eldest son of the pharaoh of the Exodus was killed in the plagues.
Num. 33:4: And the Lord did acts of judgment against their gods
1) Plague #1: Nile turns to blood. Against the Egyptian god Ha-pi, the god of the Nile.
2) Plague #2: Frogs. Against the goddess He-quet: the goddess of household affairs and fertility.
3+4) Plagues #3+4: Gnats and flies. The scarab beetle is one example of an insect considered a god by the Egyptians.
5) Plague #5: Cattle die. Against the Egyptian cow goddess, Hathor.
6) Plague #6: Boils (pus-filled abscesses).
7) Plague #7: Hail. Hail may not seem so bad to those who have never experienced it, but it can be extremely damaging and destructive. Against the Canaanite god Baal, the god of the storm (who also had worshippers in Egypt at this time) and Tefnut, the Egyptian sky god.
8) Plague #8: Locusts. Exo. 10:19: So the Lord shifted the wind to a very strong west wind that took up the locusts and drove them into the Red Sea; not one locust was left in all the territory of Egypt.
Against Shu, the god of the air.
9) Plague #9: Darkness. A darkness that may be felt
(Exo. 10:21). Probably caused by a wind-blown dust known as loess soil. Against Amon-Re, the sun god, considered the greatest god of Egypt. The pharaoh was seen as the incarnation of Amon-Re.
10) Plague #10: First born. Against the divinity of the pharaohs themselves.